Blastocyst Culture IVF
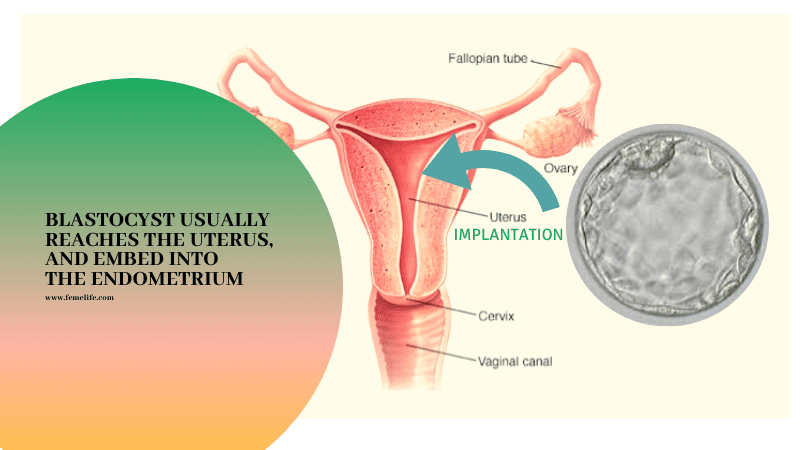
Human embryos from in vitro fertilisation in culture in an IVF lab usually reach blastocyst stage by day 5 after fertilisation. Blastocyst is an embryo which has developed to day 5 stage with different cell components and a fluid cavity. At blastocyst stage of development, the embryo must reach before it can implant in the uterus.These embryos have the best potential for implantation.
Is blastocyst good for couples undergoing IVF ?
In IVF & ICSI procedures oocytes are taken outside and good and mature oocytes are fertilized with sperms and the developing embryo is transferred on day 3 or day 5 according to the implantation rate. Compared with day 3 embryo day 5 embryo has high implantation rate because on day 5 embryologist can pick the best grade embryo and best grade embryo will be transferred and get implanted.
Is blastocyst better than embryo?
Since blastocyst is an advanced stage embryo which has outgrown its fellow embryos it has certain advantages. It has a better survival rate and greater degree of implantation potential. Recognition by endometrium is better if an embryo is healthy and is in ready to be implanted stage.
What is the success rate of blastocyst transfers?
The implantation rate for embryos transferred at day 5 was significantly higher than that for embryos transferred on day 3. Significantly fewer embryos were required for transfer at day 5 compared with day 3 embryo transfer. The high-order multiple gestation rate was significantly less with the day 5 (blastocyst) transfer than with the day 3 embryo transfer.
What does blastocyst mean in pregnancy?
Blastocyst culture offers single embryo transfer and significantly reduce the risk of multiple pregnancy. Blastocyst culture can help to determine which embryos have the best chance of being able to implant. Extended culture allows the embryologist to identify which of a group of embryos have the best potential for implantation.
Can you get pregnant with blastocyst?
If IVF does not work repeatedly with good embryos replaced on day 2 or 3, blastocyst culture can be tried. Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to treat infertility. This involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication.
Can a blastocyst turn into twins?
Your doctor prefers a blastocyst transfer in order to avoid a multiple pregnancy. However a single blastocyst transfer can also turn into a twin pregnancy. In these cases the twins will be identical and may develop with a single placenta. These twins will have more complications during pregnancy and your doctor will advise regular follow up to tackle the challenges.
Is a blastocyst considered a baby?
The blastocyst stays in their uterus for several days before it implants and while implanting embryo implants in the inner lining of their uterine wall (endometrium). It continues to make many new cells, which separate into layers. About 10 to 12 days after fertilization, the blastocyst develops into an embryo by implanting into the uterine wall. It remains an embryo until about 9 weeks after implantation, when it then becomes a fetus.
The trophectoderm helps in the growth of placenta. The inner cell mass becomes the fetus. A healthy blastocyst embryo will continue to expand and the trophectoderm then begins to hatch out of the embryo’s shell to implant in the uterine wall and become a fetus. Hatching usually occurs on day 6.
Blastocyst culture
WHAT IS BLASTOCYST?
- A day 5 embryo (blastocyst) is a cluster of dividing cells made by a fertilized egg. It is the early stage of an embryo.
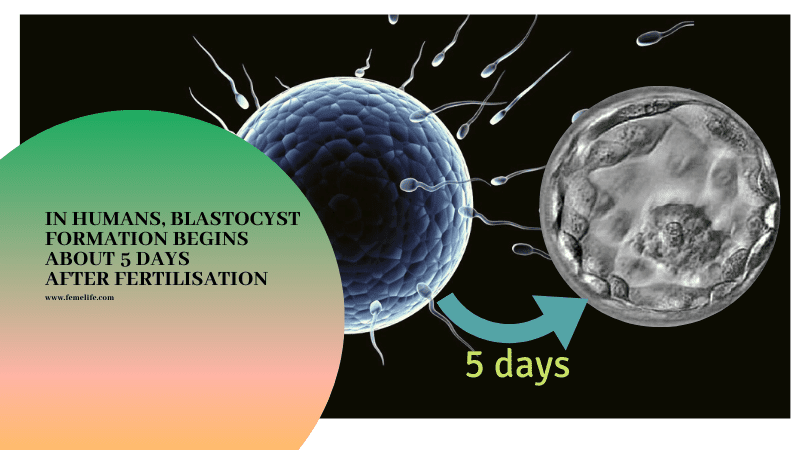
- A blastocyst forms about five to six days once sperm fertilizes an egg. Layers of cells within the blastocyst divide and separate. They eventually become the structures that protect and nourish the developing embryo.
STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT IN IVF LABORATORY:
- The day of egg retrieval is considered as Day 0 (IVF or ICSI is done once after egg retrieval)
- The pronuclear stage on day 1 (embryologist checks which eggs are successfully fertilized)
- The 2 to 4 cell stage on Day 2
- The 8 cell stage on day 3
- The morula stage on day 4
- The blastocyst stage on day 5 or day 6.
WHAT IS BLASTOCYST CULTURE?
Blastocyst culture refers to growing the embryos within the laboratory for two more days at which point they are referred to as blastocyst embryos.
WHAT HAPPENS IN IVF LABORATORY?
In the IVF laboratory, after the egg retrieval procedure, fertilization is carried out by IVF (In-vitro fertilization) or by ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection). These procedures help in fusion of egg cells with sperm and the resulting embryos are placed in an incubator. After further development embryos are transferred into the uterine cavity.
WHY BLASTOCYST CULTURE IS PERFORMED?
- Embryos that have progressed to the blastocyst stage are more likely to result in pregnancy than are embryos at earlier stages (day two, three or four embryos).
- This is thought to be a result of natural selection of the embryos, which means that the embryos that have progressed in culture to the blastocyst developmental stage are the healthy embryos of the group and capable of surviving and growing to this stage.
ADVANTAGES OF BLASTOCYST CULTURE:
- Improved embryo selection process, as it permits the embryologist to gather more information.
- Improved embryo-endometrial synchrony, which enhances the possibilities for implantation.
- Diminished risk of multiple gestation, as it allows for multiple single embryo transfers (SETs) without altering the overall pregnancy success rates.
DRAWBACKS OF BLASTOCYST TRANSFER:
- Transferring multiple blastocyst embryos can lead to multiple pregnancy because day 5 embryos have a high implantation rate.
- The major disadvantage of day 5 embryo transfer (blastocyst) is the chance that no embryos will progress to this stage. This may occur for several reasons, such as an embryo being genetically abnormal or not tolerating the artificial culture system.
WHY DO SOME BLASTOCYST FAIL TO GROW?
When embryos are cultured to the blastocyst stage in the IVF laboratory, it is usual to see about half of the embryos stop growing by the end of the 3rd day. This rate of attrition is normal and is a result of the poor developmental potential of some of the embryos.
WHO CAN BENEFIT FROM BLASTOCYST TRANSFER?
- For patients with repeated failed IVF: Performing a blastocyst culture on a patient with a history of failed IVF with day2/3 embryo transfer, can yield more information related to the growth of the embryos and aid in increasing pregnancy rate
- To eliminate multiple pregnancies: Blastocyst culture allows the chnace of transferring the single best embryo (elective single embryo transfer) and thereby reducing the chance of multiple pregnancy.
D3 & D5 TRANSFER SUCCESS RATE:
- In good-prognosis patients, day 5 embryo transfer results in increased live-birth rates compared with transfer of equal numbers of cleavage-stage embryos. Given the high implantation rate with blastocyst, eSET(elective single embryo transfer) should be routinely utilized to minimize multiple gestation.
- Blastocyst culture may be associated with an increased risk of adverse neonatal outcomes, though no causal relationship has been proven.
How many blastocysts is normal for IVF?
- Evidence supports day 5 embryo transfer in “good prognosis” patients. Consideration is warranted to transfer of a single embryo given the high risk of multiples during this patient population.
- Blastocyst or cleavage stage embryos are often used for unselected or poor prognosis patients as the pregnancy live birth rates are not significantly different, however in these populations there is a higher risk of populations there is higher risk of embryos not progressing to blastocyst stage leading to fewer/no embryos available for transfer
Extended culture allows the embryologist to identify which of a group of embryos have the best potential for however the chances of having no embryos for transfer at all are also higher.
Transferring embryos at the blastocyst stage also provides a better co-ordination between the embryo and the uterus by putting the embryo back in the uterus at the right time.