Ovulation: Anticipating A Healthy, Mature Egg

What is Ovulation?
Ovulation is an important part of female reproductive function. Women wanting to avoid a pregnancy often try to be cautious during the ovulatory days. Similarly, women pursuing pregnancy practice monitoring ovulation. Ovulation is probably the most important phenomenon when trying to conceive. Women who don’t have frequent or regular monthly cycles which means that there is a problem in their process of ovulation. This in medical terms is called as anovulation. Usually women with problem of in ovulation have difficulty in conceiving.
Human Ovary
Human ovary is the storage organ for eggs. It nurtures the eggs inside fluid filled sac called follicles. Ovarian follicles continuously undergo changes of growth, development and shedding during the human menstrual cycle. Follicles inside ovary grow when they are stimulated by a hormone called FSH releases from the pituitary gland. These follicles when are growing release oestrogen, the most important female hormone. There is a dynamic balance between these two hormones FSH and oestrogen. During the ovarian cycle one follicle matures and outgrows others called dominant follicle.
The Dominant Follicle
This dominant follicle continues to secrete the hormone oestrogen. Constant high level of oestrogen induces release of another hormone called LH. Again, this is a hormone secreted from the pituitary gland. Surge of LH is the key factor for ovulation. The ovarian follicle now disrupts and releases egg for fertilisation. After ovulation, the dominant follicle transforms into a corpus luteum. This gland again secrets oestrogen and progesterone till pregnancy. When pregnancy fails to happen it collapses, initiating menstruation.
Follicle Growth
The entire duration of human egg formation from the very early primordial phase to the pre-ovulatory phase, has been estimated to be around 6 months. This miraculous physiology begins when the baby is still inside womb. A four-month-old foetus starts developing follicles in her ovary. But these follicles containing eggs stop growing in midway giving the ovarian follicular rest. These resting follicles again start growing after the girl attains puberty. The follicular reserve goes on getting depleted till menopause. These follicular growths are a well programmed one. Some are destined to reach maturity and release egg. Whereas, others stop growing and get destroyed.
Fertility Window
The fertility window begins approximately 3–5 days (sperm lifespan) before ovulation and continues to a point approximately 1–2 days (oocyte lifespan) after ovulation.8 Identifying this window, rather than simply identifying or detecting ovulation, is vital for encouraging or discouraging contraception. For physicians or women who wish to know if a menstrual cycle is normal or to evaluate ovarian function, a test that retrospectively confirms ovulation should suffice, but for artificial reproductive techniques, the time of ovulation and the fertility window must be defined clearly.
Stages of Follicle growth and ovulation
During each menstrual cycle certain important things happen in the ovarian follicles.
- Recruitment of antral follicles
- Preferential growth of few follicle
- Selection of dominant follicle
- Release of egg from the privileged follicle
- Death of rest of the follicles.
Antral follicle recruitment
Minute follicles of 2-5 mm can be seen by ultrasound of ovary around menstruation. These are tiny follicles with minimal fluid. They show the ovarian capacity of women. It is considered normal if you have around 5 -6 of them in each ovary. These follicles are recruited 3 to 4 months earlier before they appear. These follicles stand apart from the rest of sleeping follicles. These can respond to the hormone FSH whereas others can’t. The fluid inside these follicles contain very low amount of oestrogen. Instead, they contain much more of androgens. These follicles also contain Inhibin B and AMH.
Follicle preference
Among the antral follicles in both ovaries a single follicle is selected over others. This follicle dominates and continues to grow. Usually the dominant follicle comes from each ovary in alternative months. Some times rarely, two or three follicles may dominate resulting in a twin pregnancy.
Dominance of Follicle
The dominant follicle is the one containing the maturing egg. It responds to the FSH stimulation well. At the same time, it coordinates suppression of other follicles as well. FSH hormone rises to a level till the dominant follicle is selected. Soon after it starts declining so that no other follicle attain maturity. The duration for FSH is very short in natural cycles. In IVF cycles this peak is widened so that you grow many mature follicles.
Ovulation
The dominant follicle while growing produces more oestrogen from the stored androgens. Whereas the dying follicles have more of androgen content. The hormone Inhibin B also helps in selection of dominance. These hormones increase LH release which in turn triggers ovulation. The dominant follicle grows upto 20mm size before releasing the egg.
Follicular Development in Young Girls
After birth up to puberty the follicle remains in a sleeping stage. The first few cycles during puberty may not release eggs. These are called anovulatory cycles. Slowly with the release of hormones the young girl starts producing eggs. Initial few of her cycles may show ovulation which later becomes a regular phenomenon.
Follicular depletion in elderly women: Menopause
As women grow chronologically, follicles start getting exhausted. This happens due to the regular death and depletion of eggs in each menstrual cycle. These women show few antral follicles in their ovaries. Slowly their cycles get shortened and anovulatory. In elderly women the selection of dominant follicle and ovulation happens much earlier in the cycle.
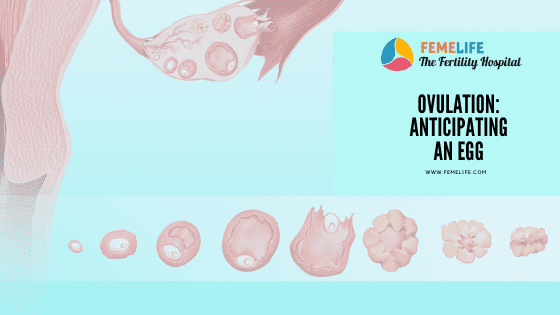
Monitoring ovulation
The best way to see the follicle growing and ovulation is to watch them through follicular ultrasound. Ultrasonography can detect the maximum growth of the dominant follicle and the subsequent decrease in size. So, the time of ovulation, can be determined from follicular monitoring. Follicular growth and ovulation detection is used in fertility treatment and artificial reproductive techniques. By detecting of the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge we can predict ovulation as well. It can be found in blood or in urine. Home detection kits of ovulation use finding LH in urine. This is useful for women who are trying to conceive. However, this is not advisable for avoiding pregnancy as sperm may survive long enough to fertilize the ovum.
Post Ovulation Progesterone
Progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum only after ovulation. Detection of progesterone or its metabolites can retrospectively confirm the occurrence of ovulation. Because progesterone causes a rise in basal body temperature (BBT), a measure of this temperature may also be useful for determining ovulation. Because the oocyte dies shortly after ovulation, methods that correlate to progesterone and its effect identify fertility window closure.
Ovulation and pregnancy
Ovulation is a process which occurs on a monthly cycle when a well matured and developed egg which is ready to get fertilized is released from the ovary and finds its path into the fallopian tube awaiting for the arrival of sperm to get fertilized. Hormones have already prepared the liner of the uterus for the potential pregnancy. If pregnancy doesn’t occur, the egg and therefore the reformed lining of the uterus are expelled through menstruation and the ovulation process occurs again.
Important Facts
Ovulation
- The lifespan of an egg after arriving into the fallopian tube is about 12-24 hours
- Typically, just one egg is released during ovulation, but quite one can occur and if fertilized leads to twins, triplets or higher, although the latter are more rare.
- Ovulation is affected negatively by suffering from illness, weight gain or loss, medications, and stress
- In Some percentage of women, they feel a mild pain during ovulation.
- Each woman is born with all the eggs she is going to ever have and as she ages the standard and quantity diminish
- Ovulation can occur albeit the cycle has not occurred
Menstrual Cycle
- A woman’s monthly cycle is measured from the primary day of her menstrual period until the primary day of her next period. on the average, a woman’s cycle is between 28 to 32 days
- Hormones are the key Ingredient in menstrual cycle regulation and ovulation.
- The follicular phase is that the first a part of the ovulation cycle. This phase starts the primary day of the last menstrual period (LMP) and continues to ovulation. This half can differ from woman to woman lasting anywhere from 7 days to 30 days.
- The secretory phase is that the second, and doubtless the foremost important half ovulation cycles.
- The secretory phase is usually only 12-16 days from the day of ovulation. This suggests that the day of ovulation will determine how long a woman’s cycle is. While stress can affect the cycle, stress round the time of the expected period won’t make it last as one’s period was already determined weeks earlier!
Can I Conceive?
Statistically a healthy few reproductive age has a few 10% chance of conceiving once per month. The woman’s age affects these odds significantly. Couples ask how soon they will attempt to conceive after stopping contraception pills and therefore the answer is true way although conception should take several months. If you’re curious about becoming pregnant, have a radical check-up by your Ob/Gyn. It’s also important to take care of healthy behaviors like eating a lower-fat diet with many fruits and vegetables, refrain or stop smoking, get regular exercise, and keep your weight within normal limits. Above all, remember to twiddling my thumbs because the process can take up to at least one year and still be considered normal.
Ovulation Time line
In a regularly cycling woman with a cycle length of 20- 30 days we can anticipate ovulation in the following way:
| Events in the cycle | Day of Cycle |
| Cycle Begins | Day 1 |
| Rise in FSH Hormone | Day 1-5 |
| Follicle grow and produce estrogen hormone | Day 5-10 |
| One of the follicle becomes dominant and produces more estrogen | Day 10-12 |
| Surge in hormone LH | Day 12-14 |
| Ovulation Occurs | Day 14- 16 |
Should I be Concerned?
While most couples succeed after a couple of months, others will wait longer. Most couples wonder when is that the time to hunt help from a fertility specialist and therefore the rule of thumb is:
- Couples 34 years and younger after one year of normal , unprotected intercourse and no pregnancy;
- Couples 35 years and older after six months of normal , unprotected intercourse and no pregnancy;
- And couples of any age with an existing medical or surgical history which will affect their fertility.
Consult a Fertility Specialist
While infertility issues impact men and ladies equally, ovulation problems are the only presumably cause for female infertility. When this happens, a woman’s Ob/Gyn may place them on clomiphene or Clomid™ counting on her age. Life of a female spans through various stages from infancy to old age. These phases like adolescence, adult hood and menopause revolve around a phenomenon called menstrual cycle. Health, mood, quality of living of the female and contribution to family depend on various aspects of menstrual cycle. It occupies around 35 to 40 years of a woman’s living. This naturally designed process is complex but smooth operating. Purpose of such a process is to provide eggs to procreate. In addition, the female is responsible for implantation, nidation and carrying gestation to deliver a healthy baby.