Adenomyosis: Best Treatment Options
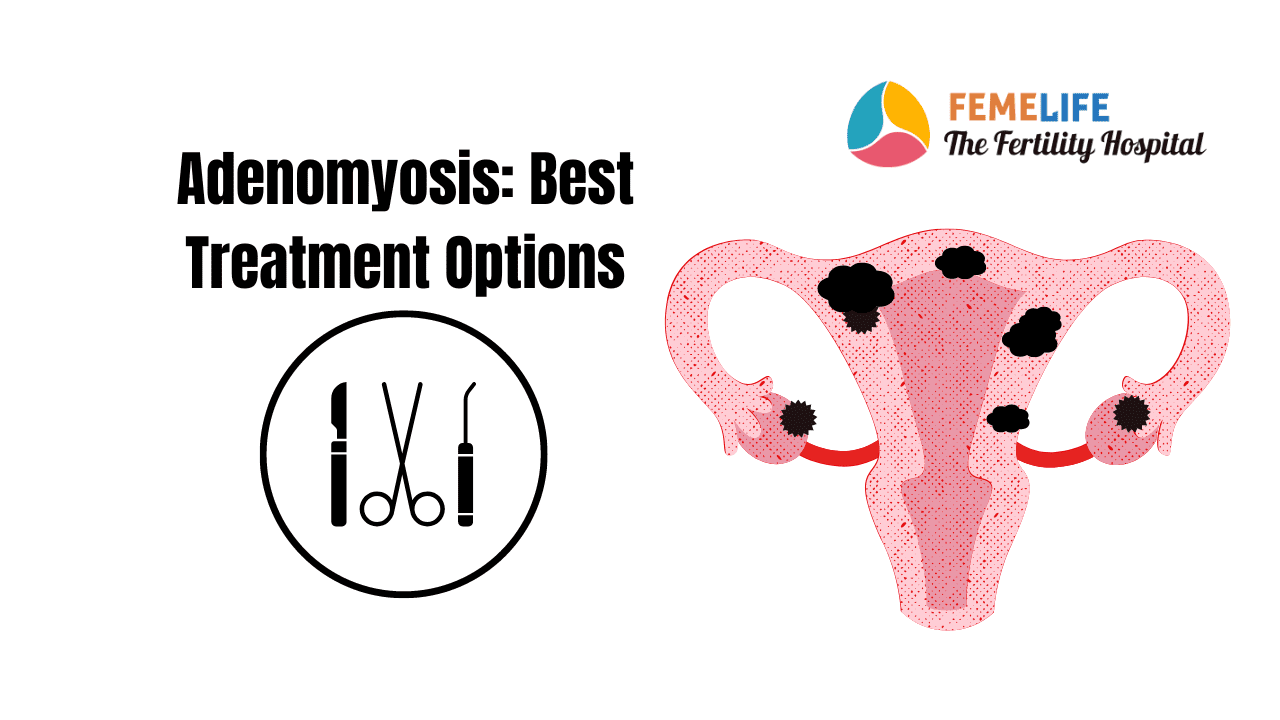
What happens in adenomyosis of uterus?
Many women suffer from severe pain during menstruation. Some of them have a condition called adenomyosis of uterus. To be precise, it occurs when your endometrial lining grows into the muscle layers of the uterus. Adenomyosis makes the uterus swollen and distorts the blood vessels leading to heavy, prolonged and painful periods. As a result, it is usually associated with painful sexual intercourse, as well as infertility in women.
Is it same as endometriosis?
Adenomyosis is different from endometriosis, where the endometrial lining grows outside the uterus. People presenting with adenomyosis may also tend to develop endometriosis. In short, it is a form of endometriosis that affects the uterine tissue. But this condition may be more painful at times and causes heavy bleeding unlike endometriosis. Adenomyosis is said to be estrogen-dependent or hormone-sensitive. It usually disappears after menopause, which takes place around 12 months after a person has a final period. Decline in estrogen levels also indicates menopause.
Is adenomyosis a serious condition?
Adenomyosis can cause minimal or no symptoms to severe pain. Some people may not experience any symptoms of adenomyosis at all. The common symptoms include:
- Prolonged or heavy menstrual bleeding
- Cramping menstrual pain
- Blood clots during menstrual bleeding
- Pain during intercourse
- Infertility
What are the main causes?
The exact cause of adenomyosis are unknown.
However, there are certain theories about what causes this condition. These include:
- Invasive growth of endometrial cells into uterine muscle may be due to incision made in uterus during surgery like removal of fibroid or a ceasarean delivery.
- The uterine inflammation that occurs after childbirth may break the boundaries of the cells lining the uterus
- Extra tissues in the uterine wall present before birth grows during adulthood
- The stem cells in the myometrium or uterine muscle wall may be a cause
Who are the women at risk for adenomyosis?
There are certain factors that cause greater risk for the condition. These include:
- Age factor : most people diagnosed in their 30s or 40s, a smaller proportion diagnosed as early at their teenage, and some diagnosed after the age of 50 years old.
- Women who have given birth before
- Those who are undergoing treatment with the breast cancer
- Other risk factors that have been suggested, but are controversial or have fewer data to support them. These include having had uterine surgery, like a cesarean delivery or removal of uterine fibroid.
- The usage of anti depressant drugs and smoking.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic evaluation includes a physician examination and imaging technique. The doctor need to perform a physical and a pelvic examination to determine if the uterus is bigger in size or tender on palpation.
In some cases, people with adenomyosis can have a uterus that is double or triple the normal size.
- Ultrasound : A transvaginal ultrasound helps the doctor to diagnose the condition while ruling out other causes of your symptoms as well. An ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of your internal organs such as the uterus in adenomyosis.
- The diagnosis of adenomyosis by ultrasound can be challenging, and the doctor may recommend more advanced imaging
- MRI scan: The best choice for diagnosing adenomyosis is the an MRI. It uses a magnet and direct radio waves to produce high-resolution images of the internal organs.
- The distinct radiologic features of the uterus that will lead a physician to suspect adenomyosis. Examples include a thickening of the area between the endometrium and myometrium of the uterus.
How can I cure it without surgery?
People with mild adenomyosis does not require medical treatment. The doctor recommends treatment options if your symptoms interfere with your day today works.
1. Anti-inflammatory medication: Anti-inflammatory medications can help to reduce blood flow during your period while also during severe cramps.
2. Hormonal treatments: Hormonal treatments can help to control the estrogen that may cause symptoms.
What are the hormonal treatment for adenomyosis?
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs like leuprolide.
- Oral contraceptives like birth control pills
- Progestin-only contraceptives like a pill, an injection, or an intrauterine device (IUD).
What is the best surgical treatment for adenomyosis?
Endometrial ablation: Endometrial ablation is a procedure that involves techniques to remove or destroy the endometrium. In addition, it is an simple outpatient procedure with a short recovery time.
Uterine artery embolization: Uterine artery embolization prevents arteries from supplying blood to the affected area. When the blood circulation is cut off, the adenomyoma shrinks. This procedure is also used to treat uterine fibroids.
Ultrasound-guided focused ultrasound surgery: Ultrasound-guided focused ultrasound surgery uses high-intensity waves to create heat and destroy the targeted tissue. The heat waves is monitored using ultrasound images in real time.
Hysterectomy: It involves the surgical removal of the uterus. Ultimately, it is considered as a major surgical intervention. For this reason, is only used in severe gynaecological cases and in people who are not planned to give birth in the future.
What happens if left untreated?
Adenomyosis symptoms can affect your lifestyle. Some people have excessive bleeding and pelvic pain. People with adenomyosis are at increased risk of anemia which causes blood loss and result in an iron deficiency.
The blood loss due to adenomyosis reduce iron levels in body. Without enough amount of iron, the body can’t make enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. Subsequently, it leads to fatigue, dizziness and inability to concentrate.